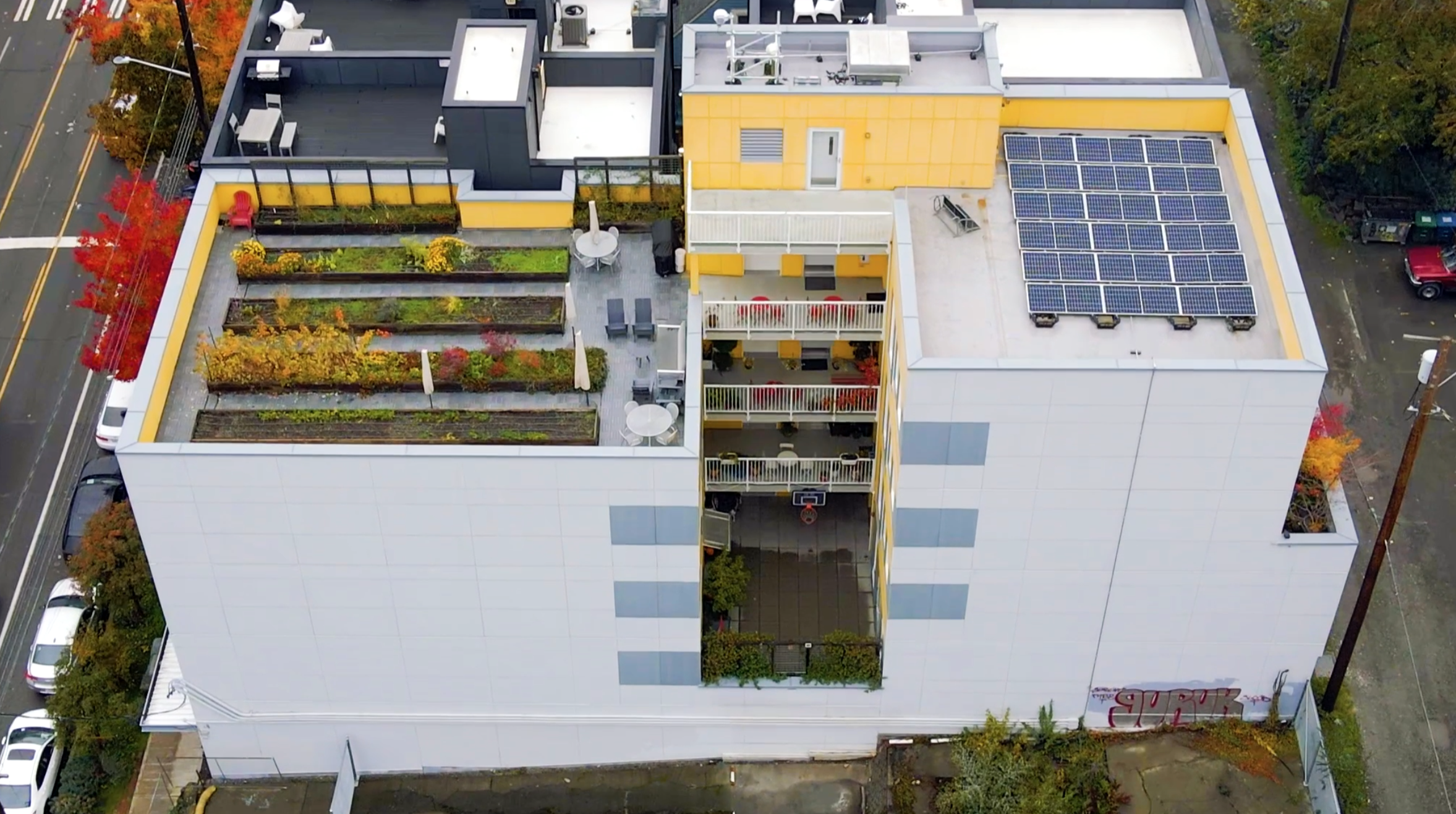
In today’s rapidly urbanizing world, resilience is no longer just a buzzword but necessary for a thriving community. At Capitol Hill Urban Cohousing (CHUC) in Seattle, resiliency is not an afterthought but an instigator for the community-built project. CHUC is a lived prototype for architects and Schemata Workshop co-founders, Grace Kim and Mike Mariano, who live upstairs and work in the street-level office space. In this 5-story building, nine households create a thriving, interdependent community rooted in shared values, meals, and mutual support. Privacy and the individual are supported by the knowing and understanding of each other. As with any group of people, it’s imperfect and requires commitment and working together. This is not just architecture or just housing, but a vision for urban living that fosters connection and resilience for generations to come.
Aerial Footage from Uytae Lee’s About Here on Youtube
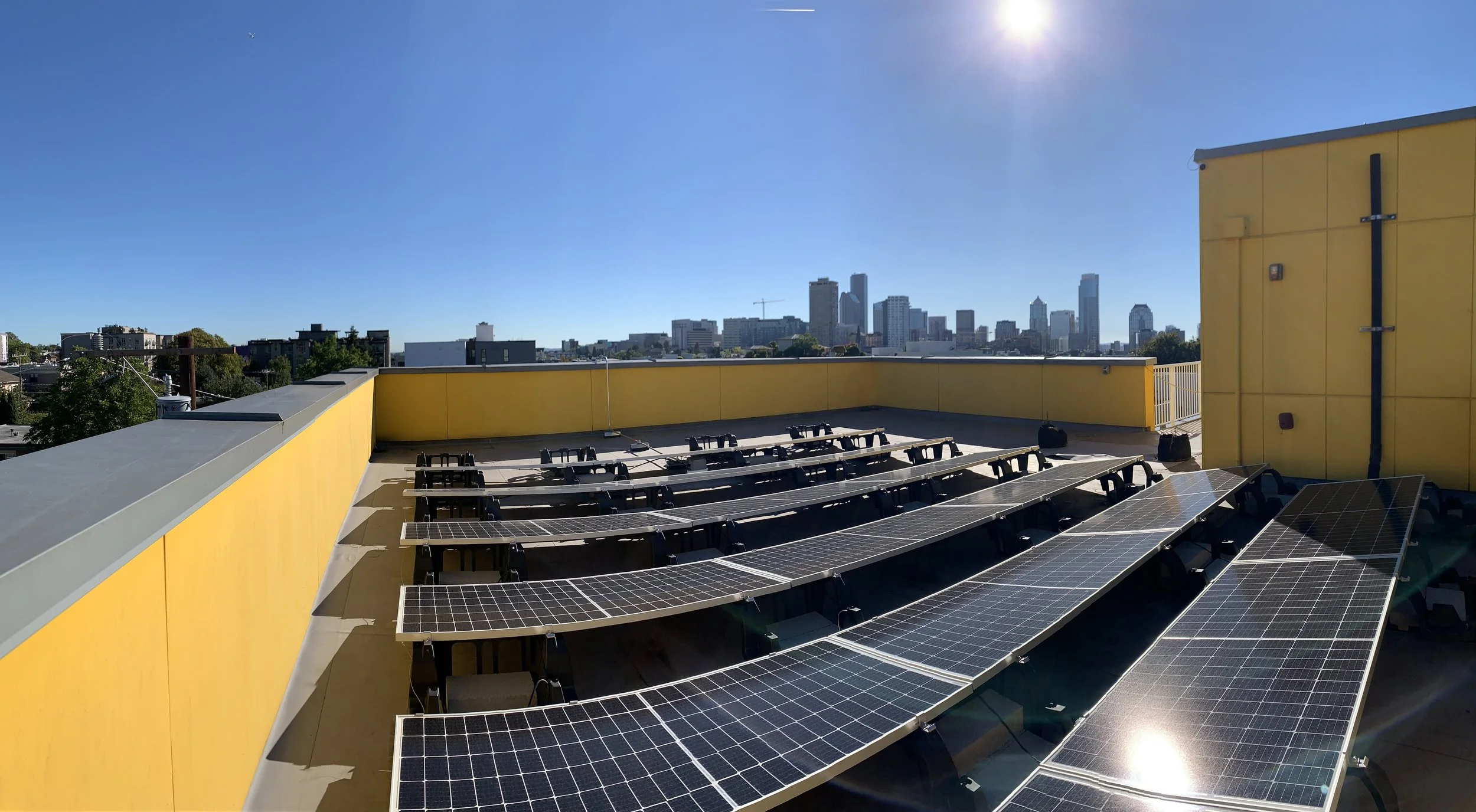
Upper roof photovoltaic for energy harvesting.
Resilience goes beyond sustainability. Grace and Mike heard an architect at an international conference once describe sustainability like a personal relationship. If I said I had a sustainable relationship with a partner, that doesn’t sound like it’s very positive. If I have a resilient relationship, then we’re able to weather the ups & downs of a relationship, and a community can be resilient during environmental shocks and stresses. Resilience is embedded in every design decision now reflected in the building that nine families have called home for nearly a decade.
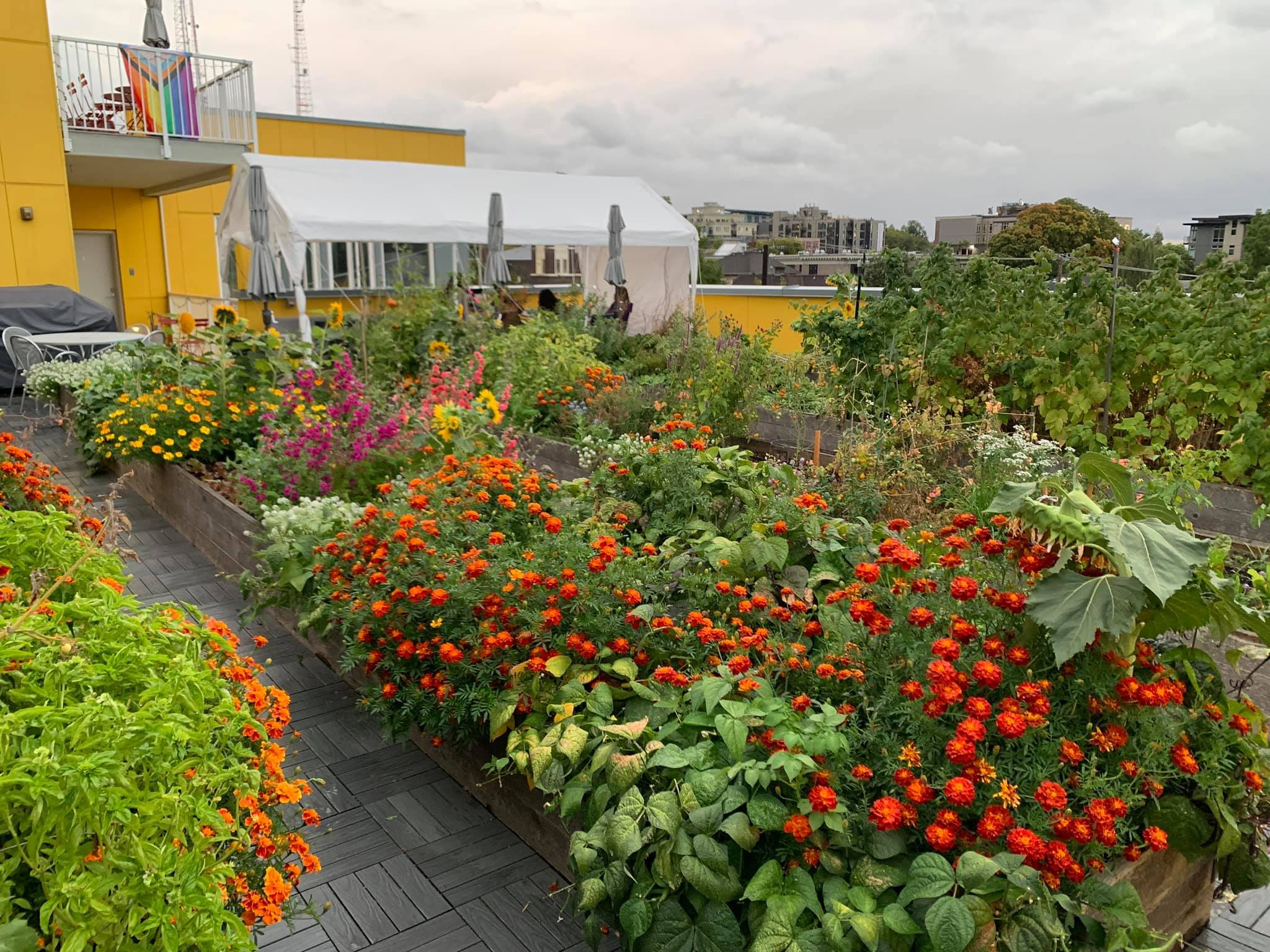
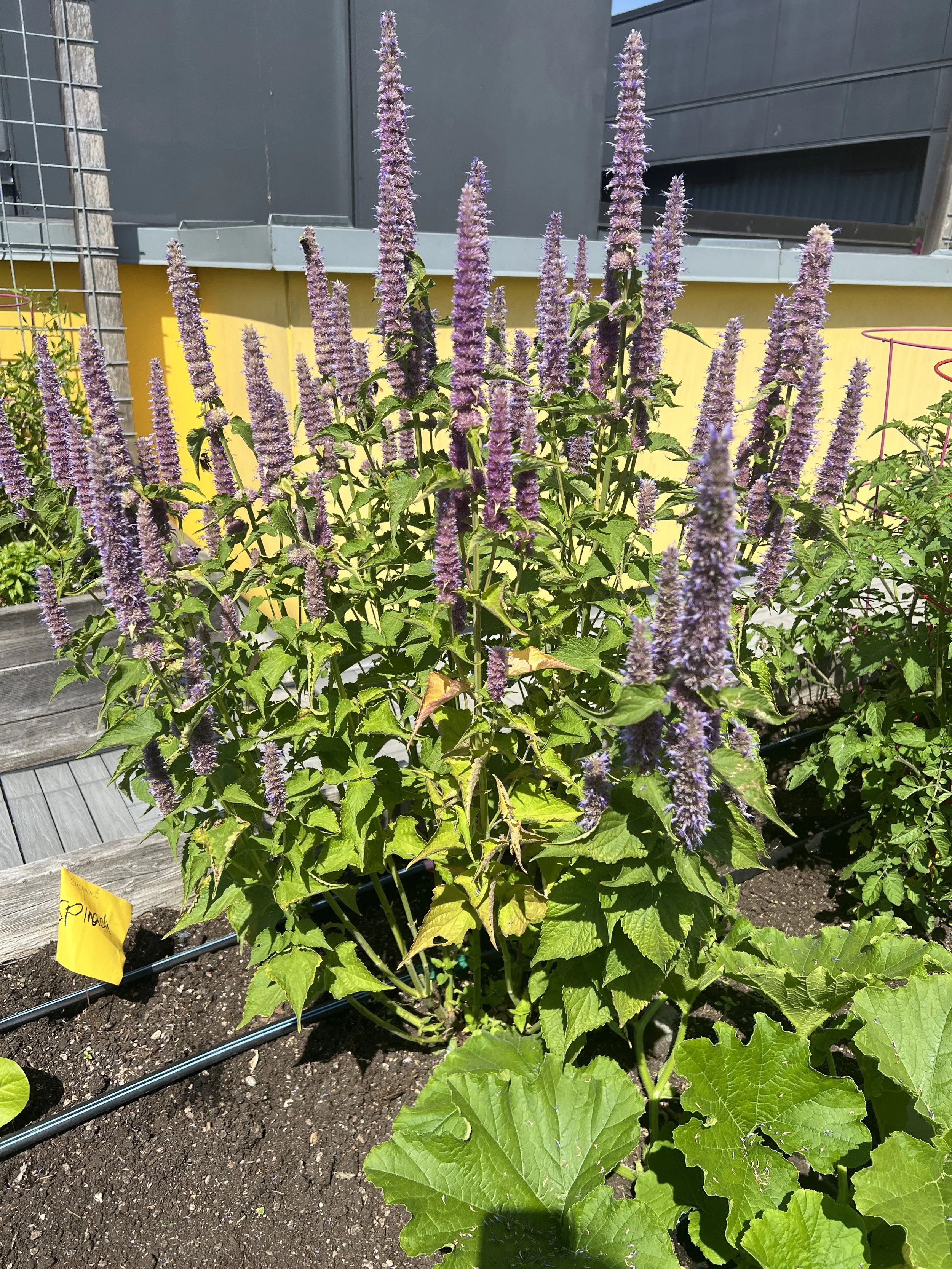
Garden roof photosynthesis for food and flower harvesting. We have a lot of happy pollinators.
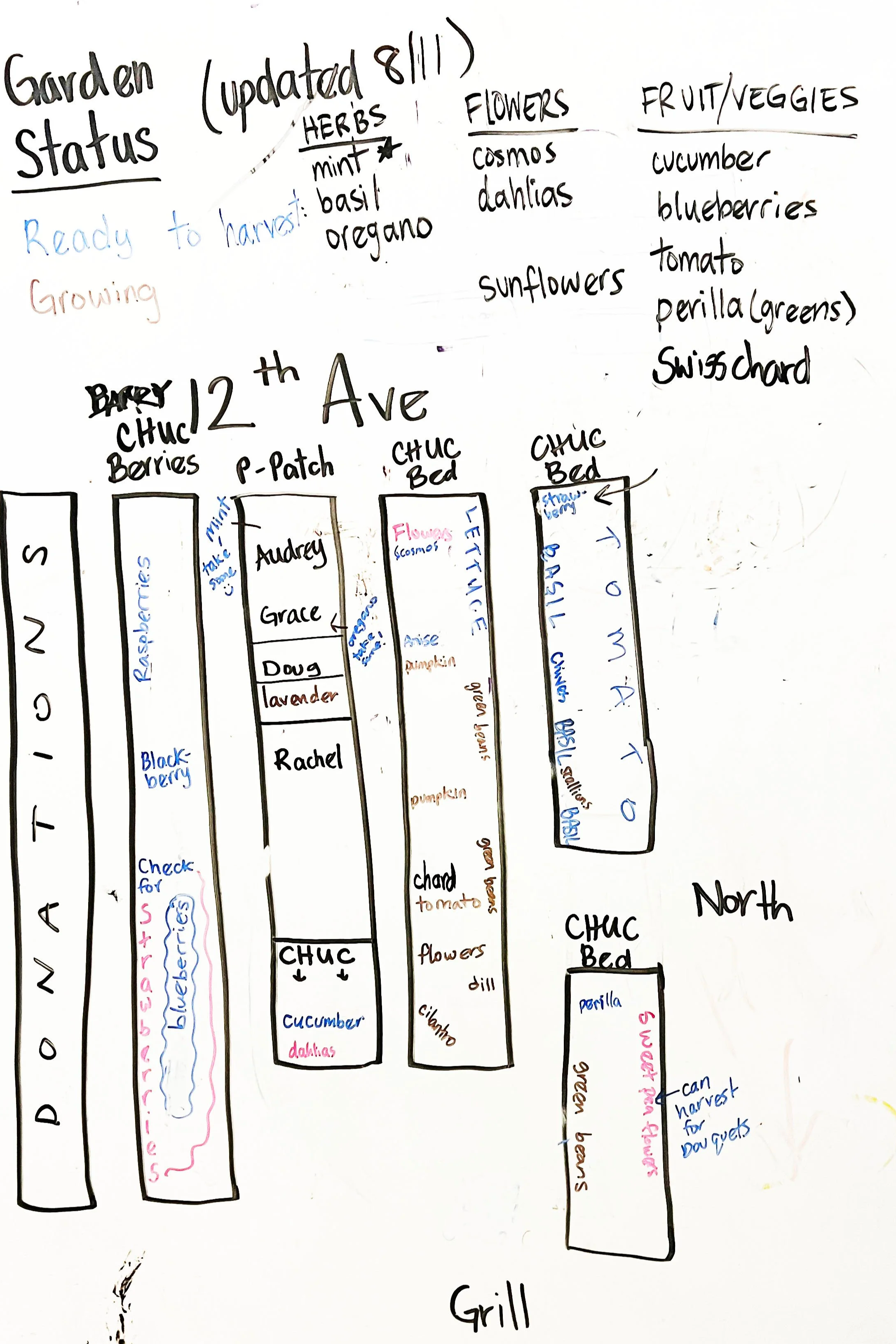
A recent post on our whiteboard for the garden reminded us of resiliency in the context of the harvest.
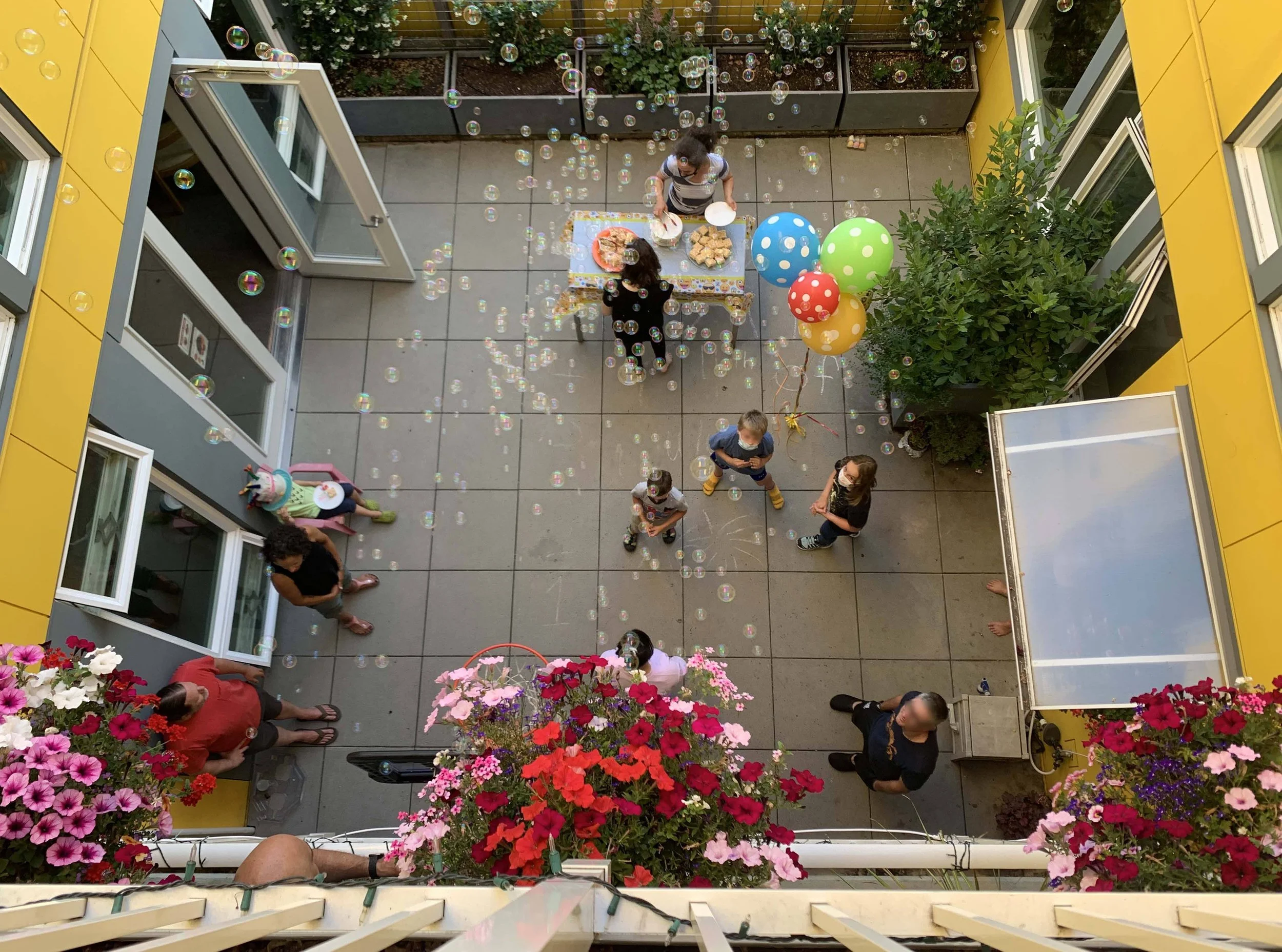
We harvest daylight through our community courtyard at the heart of our community, bringing daylight and cross-ventilation to the homes. There is no enclosed, windowless corridor here; residents move throughout the community on covered outdoor balconies. Resident life is visible in this intimate courtyard space, plants draping over balconies, the sound of resident life coming through open doors and windows, and activity on every level.
Courtyard birthday celebration (during the Pandemic - the space brought us together)
We harvest energy from the sun through the photovoltaic panels on our upper roof. We’re a small site, and the payback on solar panels is long due to our (currently) low-cost hydroelectric power provided by one of the cleanest utility providers in the nation.
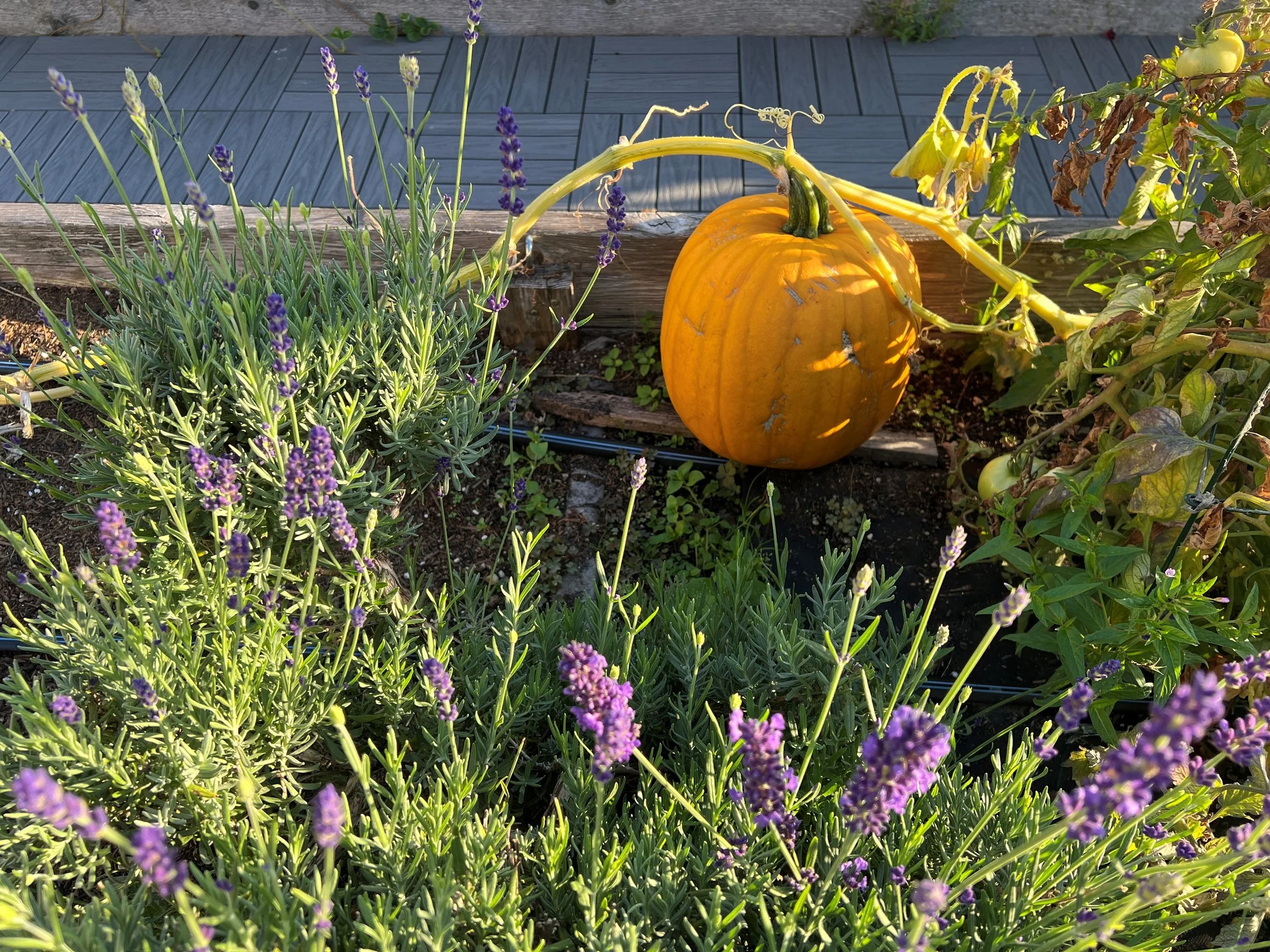
And, of course, the garden harvest on the lower roof. Photosynthesis generates fresh food that nourishes our community – produce used on site by residents, and an entire bed of produce cared for by one resident family is delivered to the nearby Byrd-Barr Place food bank.
Grace shares her lived experience and work in cohousing in her 2017 TED Talk about how cohousing can make us happy and live longer.
As profiled in the book Ideal Cities, CHUC exemplifies the kind of intentional community that contributes to the neighborhood social fabric while addressing environmental challenges.
CHUC is not just a place to live but a model of what’s possible when architecture, community, and sustainability intersect with intention.
Learn more about CHUC at our monthly Saturday tour!
Click the link and use code RESILIENCE for free tickets until the end of 2025!